
Substance Abuse
Smoking, Alcohol, Drugs
Experimentation with alcohol and drugs during adolescence is common. Unfortunately, they often don’t see the link between their actions today and the consequences tomorrow.
Common Reasons
- Boredom
- Availability
- Curiosity
- Fun
- Escape
- Rebellion / Control
- Friends
- Movies and TV Shows that glamorize drug use
- Wanting to look cool
- Peer Pressure
- Desire to alter mood
- Escape negative emotions
Body effects of alcohol
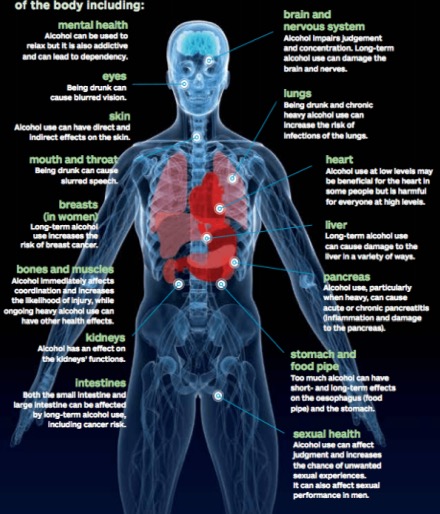
- Addiction / Dependency
- Blurred Vision
- Slur Speech
- Increase Risk of Breast Cancer
- Impair judgment
- Damage to brain & nerve cells
- Increase blood pressure
- Liver damage to FAILURE
- Reduce coordination
- Impair kidney function
- Increase cancer risk
- Damage intestines
- Acute pancreatitis
- Damage esophagus
Effect on the Brain
- The front region of the brain, the prefrontal cortex, is responsible for high-level reasoning and decision-making & does not become fully mature until the early to mid-20s.
- The prefrontal cortex - responsible for thinking, planning, good judgment, decision-making, and controlling impulses - undergoes the most change during adolescence.
- Research shows that adolescent drinking can cause severe changes in this area, which is important in forming adult personality and behaviour. It also increases the risk of mental illness.
- Damage from alcohol at this time can be long-term and irreversible.
- The hippocampus, involved in learning and memory, suffers the worst alcohol-related brain damage in teens. Long-term heavy drinking causes teens to have a 10% smaller hippocampi, short-term or moderate drinking impairs learning and memory, and frequent drinking inhibits systems crucial for storing new information.
Liver Damage
- Alcoholic liver disease accounts for over a third of all liver disease deaths every year.
- When alcohol reaches the liver, it produces a toxic enzyme called acetaldehyde which can damage liver cells and cause permanent scarring.
- Leads to: Alcoholic hepatitis, fatty liver, cirrhosis.
- It can also lead to loss of brain function that occurs when the liver cannot remove toxins from the blood. Toxins reach the brain and cause symptoms like extreme confusion, altered levels of consciousness, coma, and even death.

Stages of Use
Non Use
The use of no substances.
Experimental Use
Trying a substance a few times.
Occasional Use
- Once in a while
- Not regularly done
- Not getting drunk every time
Regular Use
- Routine
- Part of a pattern, i.e. every weekend, every other weekend
- Doesn't get drunk every time
Abuse
- Use interferes with functioning
- Loss of control over the amount one uses/intends to use
- Loss of control over behaviour
Dependency
- Addiction
- Compulsion
- Extreme change in attitudes, behaviours and feelings
Consequences that drinking alcohol can have
(Result of your drinking and others' drinking):
- Hangovers
- Academic problems--missed classes, getting behind in school work
- Arguing with friends
- Weight gain
- Getting injured
- Damaging property or having your property damaged
- Requiring treatment for alcohol poisoning
- Trouble on campus or with police
- Being insulted or humiliated
- Having your study or sleep interrupted
- Developing tolerance, dependence or addiction
- Death from alcohol poisoning or alcohol-related injury
Nutritional content of Alcohol:
- Smirnoff Ice Premium Vodka Beverage (12-ounce)
Calories: 245
Sugar: 32 grams, which is equivalent to about 8 tsp of sugar - Bacardi Breezer Rum Beverage (275ml)
Calories: 100 - Vodka and Rum (shot - 1.5 fl oz)
Calories: 97 - Whiskey (shot - 1.5 fl oz)
Calories: 105 - Tequila (shot - 1 fl oz)
Calories: 64 - Beer (bottle - 330ml)
Calories: 144
One in seven (14.2%) of Canadians aged 15 years and older experienced at least one of these harms due to another person's drinking.
- Verbally abused
- Being emotionally hurt or neglected
- Feeling threatened
- Being physically hurt
SOCIAL MEDIA - cell phones
Due to social media, the majority of our lives get captured and posted online. Once it's on the internet – it's there forever. Parents can see, future employers, classmates, family etc. It can lead to anxiety, bullying, and depression.
Alcohol Related Dangers
- 696,000 students between 18 and 24 are assaulted by another student who has been drinking.
- 97,000 students between 18 and 24 report experiencing alcohol-related sexual assault or date rape.
- Post effect of Trauma can lead to an increase in mental health issues (anxiety, depression, PTSD)
- About 1 in 4 college students report academic consequences from drinking, including missing class, falling behind in class, doing poorly on exams or papers, and receiving lower grades overall.
Vomiting
- It is common for someone who drinks excessive alcohol to vomit since alcohol irritates the stomach.
- Alcohol depresses nerves that control involuntary actions like breathing and the gag reflex (which prevents choking).
- Overdose of alcohol will eventually stop these functions.
- Danger: choking on vomit could cause death by asphyxiation in a person who is not conscious because of intoxication.
Group activity:
You are at a party, and your friend drank one too many. In the washroom, partly unconscious, they begin to choke on their vomit. What do you do?
Some solutions
Party pressure
- ''I’m driving.''
- ''I haven’t eaten yet, and I don’t want to drink on an empty stomach, maybe later.''
- ''I’m actually having a great time already, thanks. I’ll let you know if I want any.''
School Buzz
- ''I really don't like smoking pot - it just makes me really anxious.''
- ''I’ve got a test next period, and I need to keep my head clear.''
- ''I’m exhausted - let’s go to the convenience store and get some coffee instead.''
Drunk Driver
- ''Since I'm sober, just let me drive.''
- ''Let me see if someone else is here who hasn't been drinking and could give us a ride.''
- ''You're too drunk right now. Let's walk for a while and talk - we can figure out how to get home later.''
Alcohol and/or Drugs in Fatal Motor Vehicle Crashes
Researchers estimate that each year:
- 1,825 students between 18 and 24 die from alcohol-related unintentional injuries, including motor-vehicle crashes.
- Not only can you harm yourself, but you can harm others
Drinking and driving is a crime under the Criminal Code of Canada. You may:
- lose your license
- have your vehicle impounded
- need to pay an administrative monetary penalty
- need to attend an education or treatment program
- be fined upon conviction
- be required to install an ignition interlock device in your vehicle
- spend time in jail
- end up with a criminal record
If you are caught with a blood alcohol level of 0.08 or more for the first time, you will have an immediate roadside 90-day suspension, 7-day vehicle impoundment and a $550 penalty. If you are caught again, the penalties only get more severe.
How to say no
What are some ways you can say no to drinking alcohol or reduce alcohol-related dangers?
- Drive smart – Uber, be the designated driver and don’t be afraid to take away someone’s keys for the night.
- Coping - cyberbullying, school stress, family stress, to relax, deal with anxiety.
- Finding healthier ways to cope – counselling, exercise, hobbies and doing more things you enjoy, deep breathing, talking to someone.
- Don’t give in to peer pressure. Be a leader, not a follower.
Smoking causes...
- More than 480,000 deaths each year in the US (almost 1 in 5)
- Approximately 48,000 deaths each year in Canada
- Nutritional deficiencies (i.e. Blocks vitamin C)
- Addiction to nicotine
- Cancer
- Decrease in physical fitness in both performance and endurance.
- Life expectancy for smokers is at least 10 years shorter than for nonsmokers.
- Smoking damages blood vessels and can make them thicken and become narrow. This makes your heart beat faster, and your blood pressure goes up and increases the risk of blood clots.
- Quicker decrease in bone density – easier fractures, breaks, risk of osteoporosis
Vaping
- The FDA has found a potentially deadly antifreeze chemical called diethylene glycol in an electronic cigarette cartridge and some vape flavour liquids, along with tobacco-specific nitrosamines, which are linked to cancer.
- Often still contain nicotine (heavily addicting)
Why people smoke
- Boredom
- To look cool
- Stress
- Habit/addiction
What to do instead
- Sip on a non-alcoholic drink (social outdoor ‘smoking’)
- Deep breathing
- Chew gum (ween off, anti-stress, focus)
- Anti-stress: do more things you enjoy, find your triggers, stress balls
- Exercise
- Talk
- Listen to music

Substance Use
Alcohol and/or drugs use causes a temporary “high,” which eventually leads to “crashing” or “coming down.”
A drug “high” lasts a short time, depending on the drug and dose. The changes in the brain that result from continued drug use can be permanent.
How Does Marijuana Affect a Person's Life?
Compared to those who don't use marijuana, those who frequently use large amounts report the following:
- Lower life satisfaction.
- Poorer mental health.
- Poorer physical health.
- More relationship problems.
- People also report less academic and career success. For example, marijuana use is linked to a higher likelihood of dropping out of school. It's also related to more job absences, accidents, and injuries.
Effects of Marijuana
Short-term effects
- Short-term memory problems
- Severe anxiety, including fear of being watched or followed (paranoia)
- Panic
- Hallucinations
- Loss of sense of personal identity
- Lowered reaction time
- Increased heart rate (risk of heart attack)
- Altered judgment (often leading to violence, danger, and injury)
- Impaired motor coordination, interfering with driving skills and increasing the risk of injuries
- Sexual problems (for males)
- Up to seven times more likely to contract sexually transmitted infections
Long-term effects
- A decline in IQ (up to 8 points if prolonged use starts in adolescent age)
- Poor school performance and a higher chance of dropping out
- Impaired thinking and ability to learn and perform complex tasks
- Difficulty learning
- Lower life satisfaction
- Addiction
- Relationship problems, intimate partner violence
- Antisocial behaviour includes stealing money or lying
- Financial difficulties
- Increased welfare dependence
- Greater chances of being unemployed or not getting good jobs

Marijuana also affects brain development
One study found that teens who regularly use marijuana lose an average of 5.8 IQ points by the time they reach adulthood.
Side effects of drugs
- Memory loss
- Hallucinations
- Anxiety and depression
- Seizures
- Dehydration
- Slowed heart rate
- Distortion of reality
- Emotional swings
- Long lasting confusion
- Sleep problems
- Paranoia
- Impaired mental function
- Poor motor coordination
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness, nausea
- Aggression
- Disturbing thoughts
- Inability to perceive danger
- Hearing voices
- Brain damage
- Loss of control
- Stroke
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Death
Tolerance
Tolerance is one of the first changes in the brain that occurs in response to repeated drug abuse.
Tolerance develops when a person needs increasing doses of a drug to achieve the same "high" or "rush" resulting from a lower drug dose.
This repeated use leads to permanent changes in the brain and dependence on the drug. Drug abuse and dependency are considered a disease and deadly if not cured.
I.e. Initial amount to produce effect to Amount needed to produce effect










Don't see what you're looking for? Send us an email!
©Copyright 2024 Cam’s Kids powered by Kids Help Phone
Not-for-Profit Organization. B/N: 921508-5
Thanks for visiting Cam's Kids. Please remember...
Cam's Kids is not a service provider.
If you are in crisis, please call 911 or go to your nearest emergency department. For free, confidential counselling, contact Good2Talk or Kids Help Phone.
Post-secondary students: find your local crisis resource here.



